What Is a Checksum, and What Can You Do With It?
You're near to click on a download button and notice a weird looking lawmaking side by side to it. Information technology doesn't seem to have anything to practise how big the file is or whether it's something that you should make a note of. And so you lot get ahead, get the file, and disaster! Information technology doesn't seem to be the same as what you lot expecting.
If just in that location was a quick mode to see if that the detail yous've just downloaded is exactly the same equally the file that was on the website. Well, there is. Welcome to the globe of checksums!
Just what the heck is a checksum?
TL;DR: A checksum is a number, in the grade of a binary or hexadecimal value, that'due south been derived from a data source. The important bits to know: a checksum is typically much smaller than the data source, and it's also nearly entirely unique. Meaning that the chances of another data giving exactly the same checksum is extremely unlikely.
Let's have a await at some examples, the commencement of which is a elementary text file (beneath), containing some disquisitional information! All files incorporate information that embrace more than but than, say, the text we can see -- at that place will be bits allocated to telling us what blazon of file it is, how the information is arranged, and and so on...
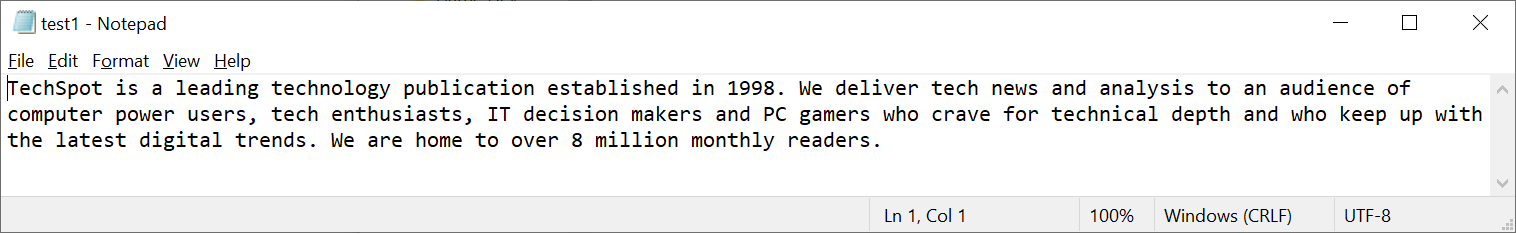
All of this gets handled in the process of creating the checksum, and we'll show you how it works and how you can do it yourself subsequently in this article.
But for now, let'south have a await at the value we get:
798B38084999FA50E7D1861E07E45F4E3AA39668DC6A12A84A058CAAA32DE0EB
Past itself, that code doesn't tell us anything. Nosotros tin can't reverse 'hack' it to figure out what the pattern of the ones and zeroes that the text file consisted of. Nonetheless, information technology is supposed to be specific to that detail file, so now let's alter the original text file by rearranging some of the words.
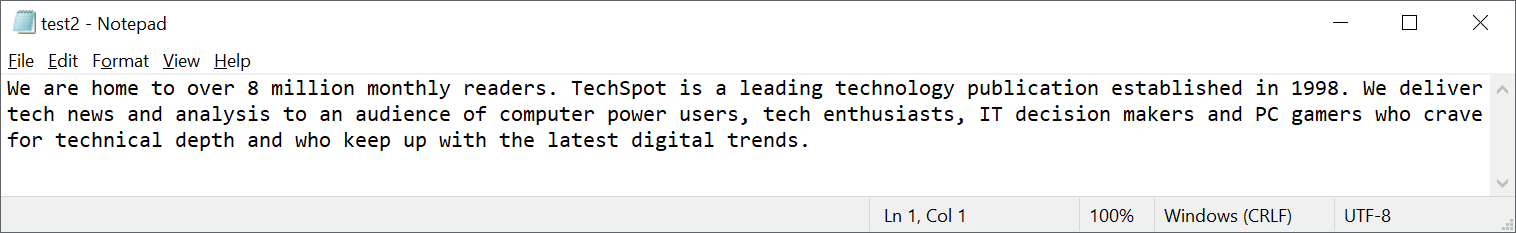
The paradigm above clearly shows that information technology'due south still the same text, and and so technically the same data, merely the sequence of the $.25 is at present different. And the checksum this time round is:
22698AA81AFF43B48ADA1BCC7E26D641F0077C0AA24B5B19C8C801147A41B30D
Find how it'southward the same length -- this is a cardinal aspect of the process of getting the code -- but it'south entirely an different checksum. Same data, dissimilar society, totally new checksum.
But perhaps that should take been expected; after all, the changes to the file weren't entirely trivial. So let's see what happens when nosotros change just one letter in the whole affair: encounter if yous can spot which i!
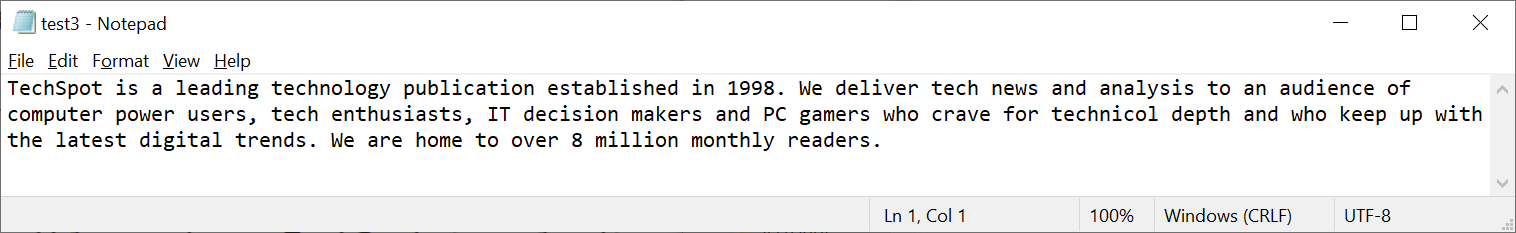
Cue the drum roll in the groundwork, every bit we look at the checksum for this barely altered file.
790DD6BF0733981E4EBF9BA116970D943D91C2CDD3531CF877E30F3E92F29453
That alter of just one alphabetic character has once again given us another unique lawmaking. When information technology comes to checksums, that'due south the whole point of the system: any changes to an original data source, no matter how small they are, should result in a wholly new checksum, and making it extremely like shooting fish in a barrel to see if something has been altered.
With that out of the way, let's meet how it all works then!
The tech backside the check
At the middle of a checksum is the software algorithm that'south used to create the codes we saw. In the case of our examples, nosotros used a very common ane known as SHA-256 (Secure Hash Algorithm - 256 bits). This algorithm is a blazon of cryptographic hash role (CHF), with the source data labelled as the message, and the output being chosen the hash value or just hash (the checksum, in this case).
Developed past the NSA and released nearly xx years ago, SHA-256 belongs to a class of CHFs that are in widespread use effectually the world. Their popularity is down to the fact that they work speedily and they're resilient confronting attempts to 'hack' the code -- although there are much better ones available these days.

Each algorithm has its own way of doing things, but we'll just focus on what SHA-256 does. The process ever gives a hash of a fixed length (256 $.25 in this case), regardless of how big the message is, although technically it's actually 8 values, each 32 bits in size.
So the checksum for our test1 file is really 798B3808 4999FA50 E7D1861E 07E45F4E 3AA39668 DC6A12A8 4A058CAA A32DE0EB. This has been written in hexadecimal -- writing it out as a string of 256 ones and zeroes would be very slow!
The first stride in algorithm'southward sequence is to procedure the bulletin, then that's a drove of blocks, each 512 bits in size. For files that aren't whole number multiples of 512, or if the file is smaller than this size, a trick called padding is employed. This is where a whole stack of zeroes are added after the message's bits are finished, to make it a circular 512.
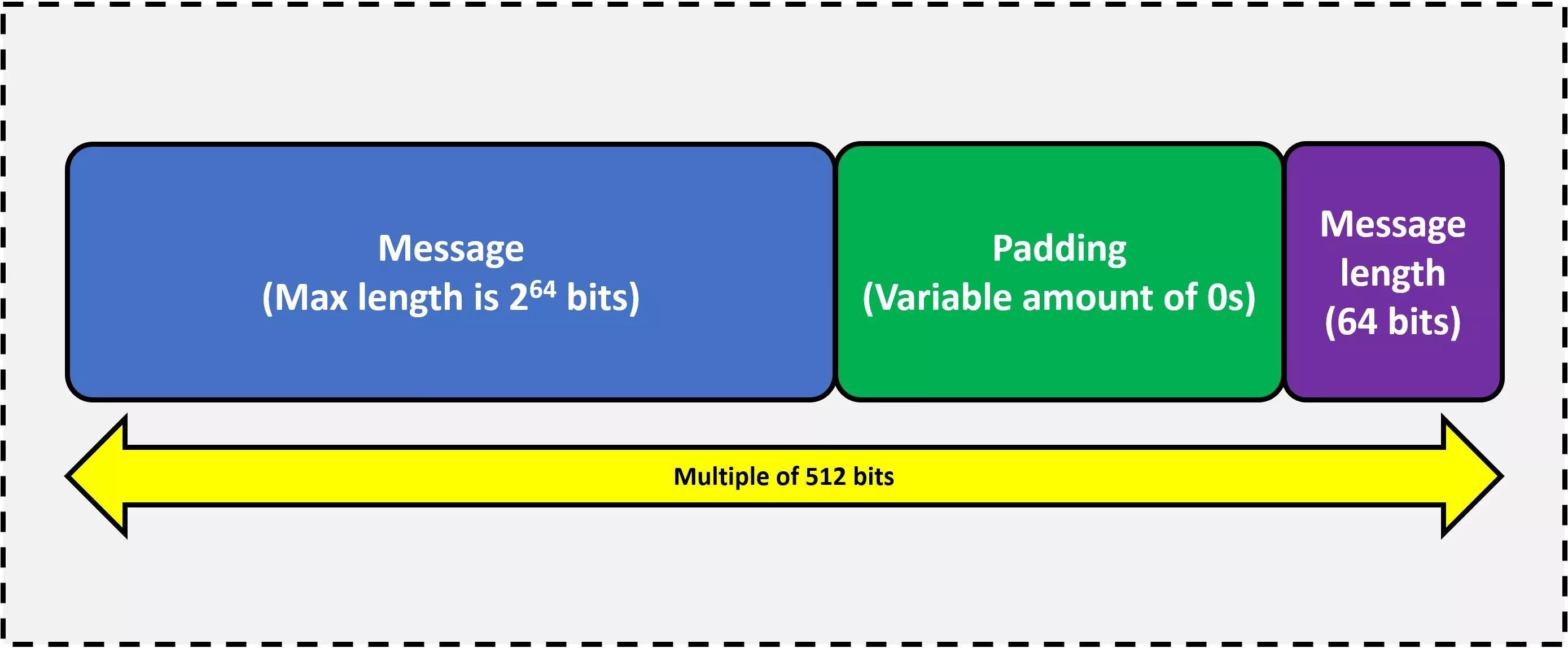
For example, permit's say nosotros're trying to find the checksum of a file that's 10145 $.25 in total size. This would piece up into 19 whole blocks, leave 417 bits left over to fill. To indicate where the information ends and the padding starts, the string of bits that makes up the source has a ane added to the end. And so here, the padding would add 352 zeroes.
Hang on, why isn't it 416? The very concluding portion of the last block is a special 64-bit number: the length of the original file. That means, for our example, the 20th block would have to finish with the binary value of 10145, resulting in the message only requiring 402 bits of empty space to fill.
Once that'due south done, the algorithm takes the very first 512-bit cake and slices it up into xvi portions, each i 32 bits in length; each of these values will be used in the hash calculation procedure.
Up until this signal, this is the easy part: the remainder of process involves a lot of math.
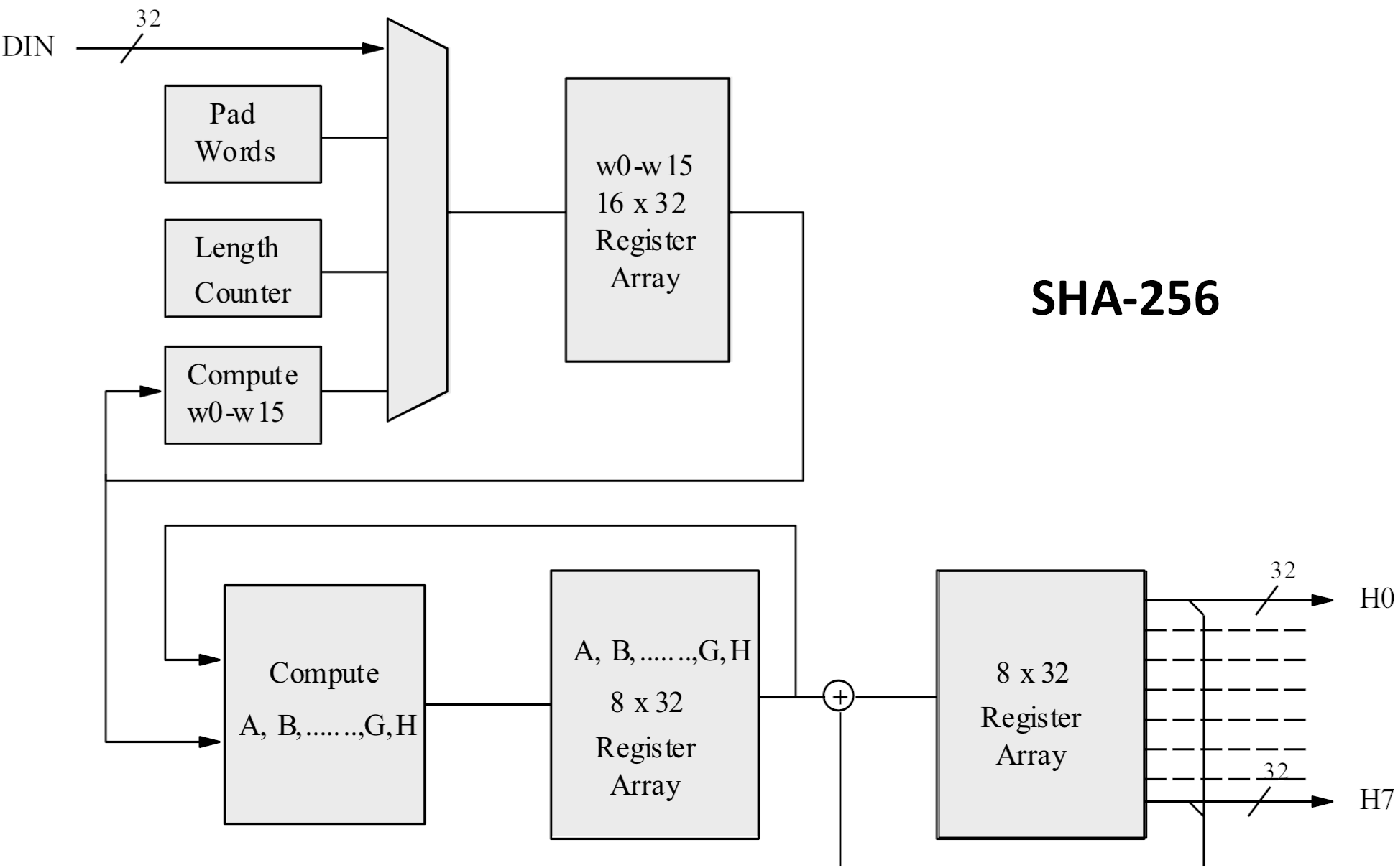
It'due south all well beyond the telescopic of this article but if yous're interested in earthworks into it in more than detail, you lot can read more than about information technology hither. Simply to give you a cursory overview, it involves creating a starting hash first, using the outset 8 prime numbers. These are run through an equation to requite a 256-fleck long value that'due south and so modified over and over, equally the remainder of the algorithm works its way through all of the portions, in every block, from the processed source data.
Sounds horribly complicated, yes? For a modern CPU, though, information technology's a slice of block.
Information technology takes no more than a dozen or so processor cycles, for every byte of source data, to generate the hash.
Then what can you lot do with a checksum?
TL;DR: A checksum allows you to easily bank check the integrity of the information that makes upward a file.
Picture this scenario: you need to download an important file, that'due south critical to operate a computer. Actually critical, so much so, that you lot don't want it to have any errors or glitches in it. You've also got a slow and unstable internet connection, and you're worried that it might touch the file equally it downloads.
The host of the file knows all of this, so they run a checksum algorithm on the file and put the answer on the download webpage. One time you've got it, yous tin run the same process and compare the values -- if they're the aforementioned, you'll know the file you lot downloaded is all okay.
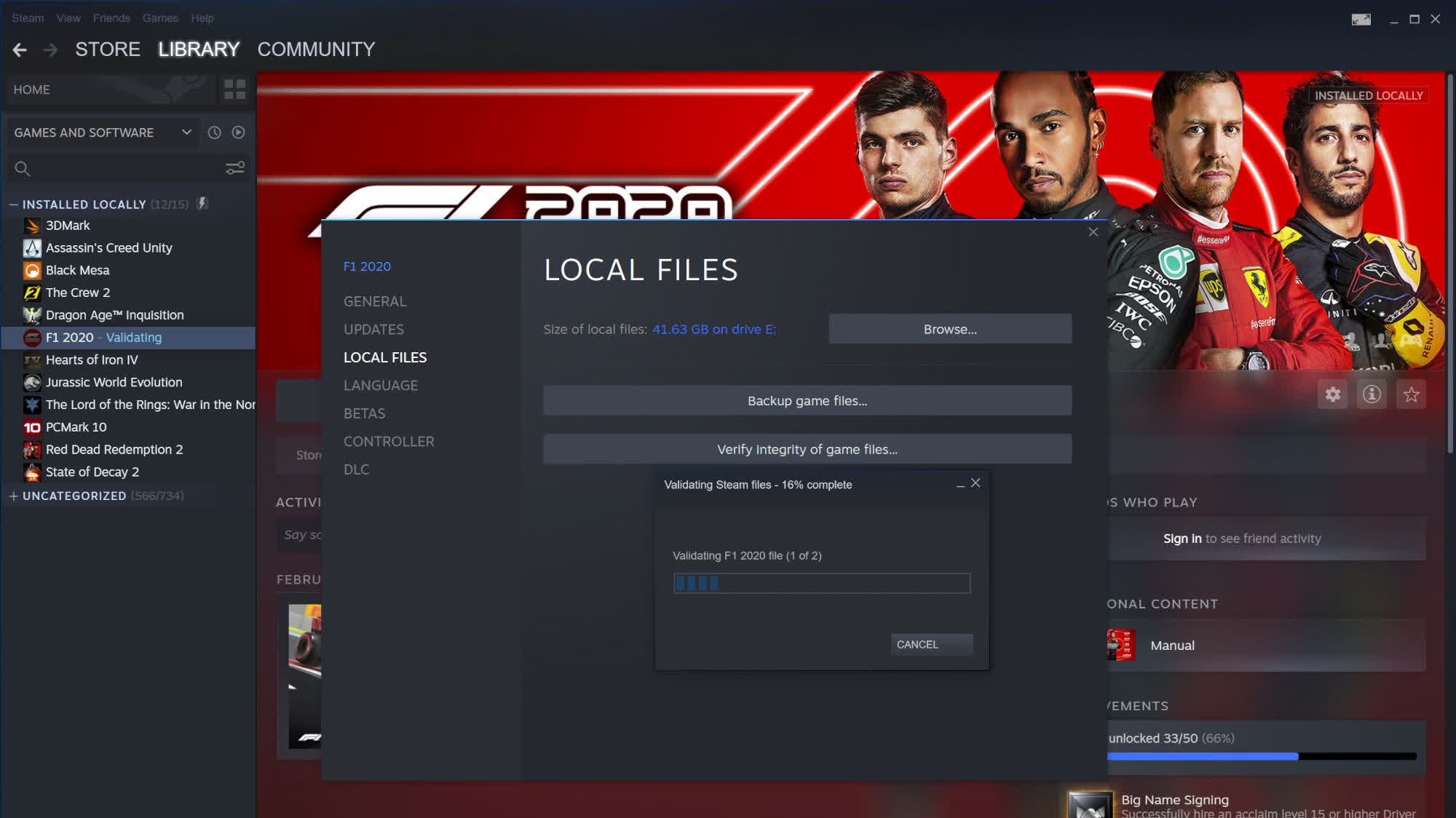
And this is primary use of a checksum: checking the integrity of the data that makes up a file. It tin can exist done manually, as we'll encounter very shortly, or information technology tin be part of an automatic performance. Valve uses checksums on the Steam platform equally part of the file verification process.
Run your ain checksum
All of the major operating systems take a built-in checksum tool, also.
Windows
To run a checksum in Windows, the easiest mode is to utilize PowerShell: correct-click on the First Menu button or press Win+X. If y'all're running an older Windows version, you tin download PowerShell from here.
Enter the command get-filehash followed by the file location. Alternatively, enter the command then drag and drib the file into the PowerShell window. Here's how our first test file was done.
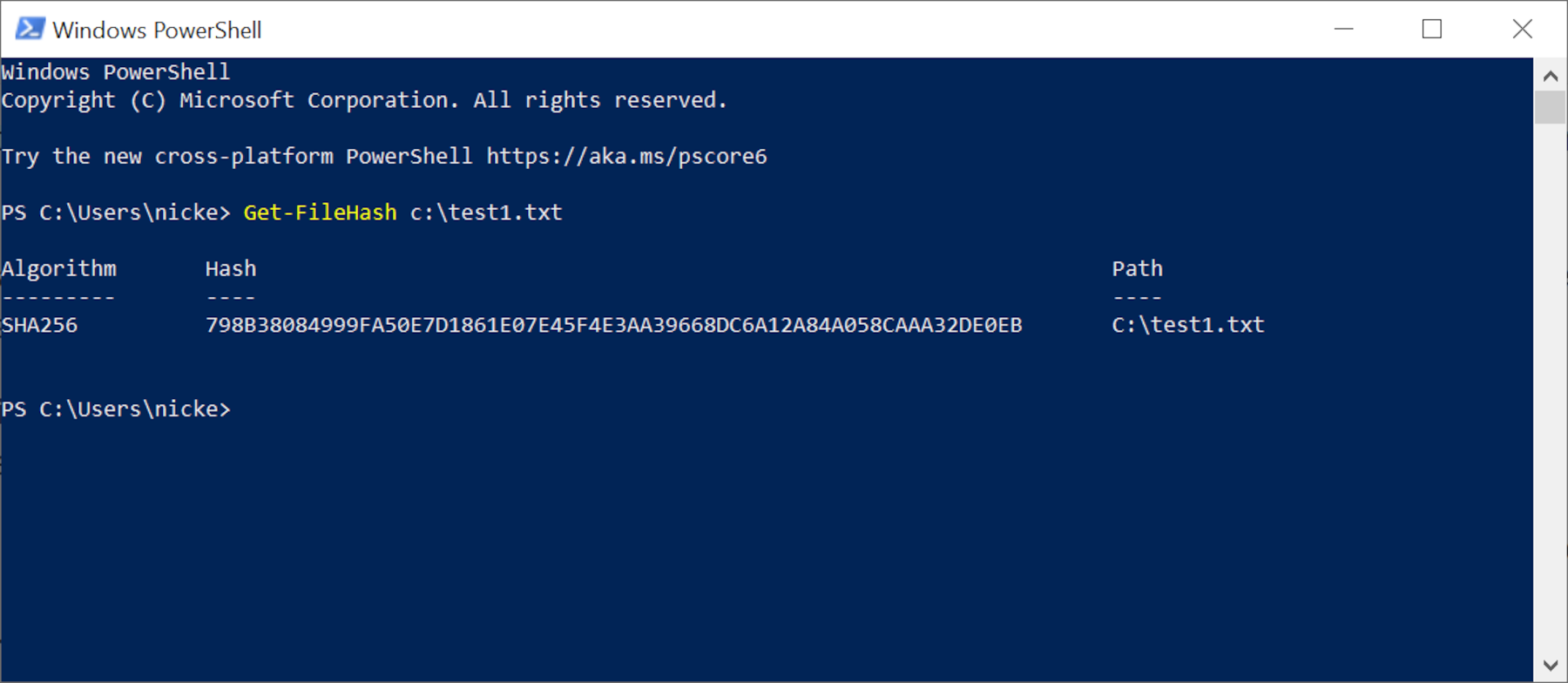
Past default, PowerShell uses SHA-256 to produce the checksum, but you can use others such as SHA-512 or MD5. These will all produce a different hash, but it will still be unique to that file. To employ a unlike function, add together the control -algorithm followed by the code for it.
For checksums, using a unlike hash part doesn't bring whatsoever significant benefits, although some of the older ones (e.one thousand. MD5, SHA-i) take been shown to produce the same hash for different files -- an issue that'southward known as a collision. Newer algorithms are more resilient to collisions, which is why PowerShell defaults to SHA-256.
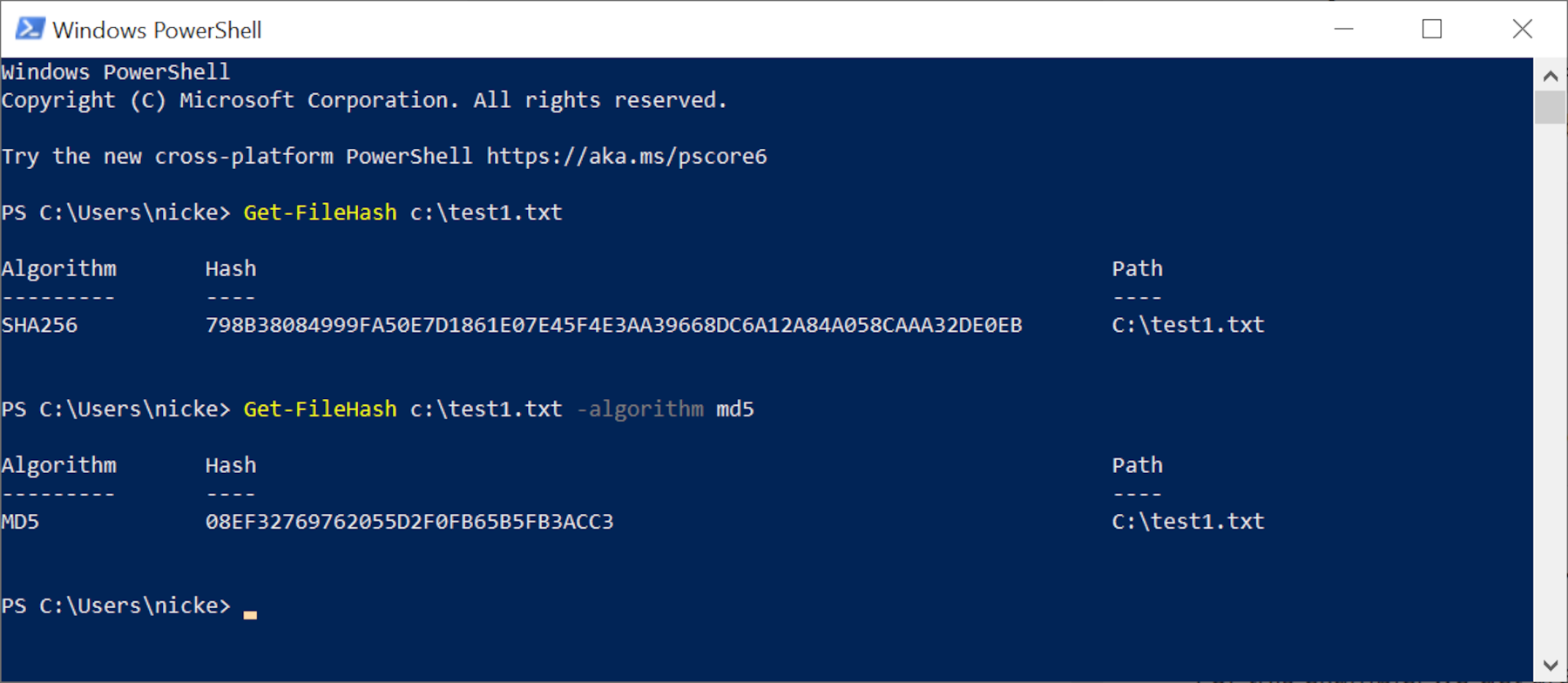
The principal reason for needing to switch to a dissimilar function is downwardly to the file host choosing to utilise something other than SHA-256, so yous'll demand to switch to this, in order to compare the files.
Comparing two long strings of numbers and letters can be a bit difficult to exercise, merely with a tiny bit of programming, you can make PowerShell evaluate the checksums for you. Let'south use the to a higher place MD5 code as an example and pretend that the original file's hash actually ended with the number 8.
The epitome beneath shows the lines of code yous need to input, using Shift+Enter after each one.
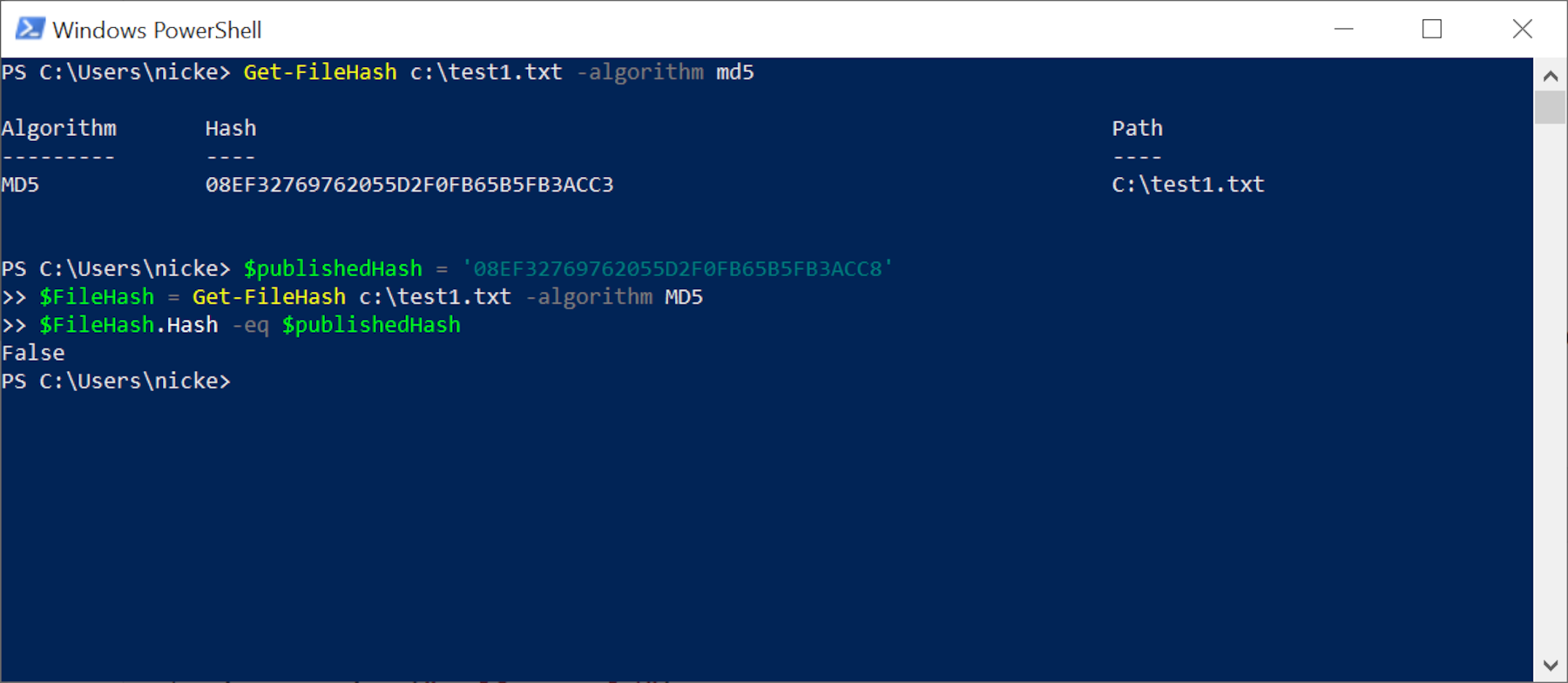
See how it says 'Simulated'? That'due south telling y'all that the file isn't the same. If you're certain that you have the correct hash for the file you want, and then all suspicion falls on the data.
Note that a checksum can't tell you how the files are unlike -- it's a very binary test, if y'all pardon the pun. But it's a useful tool and there some very specific checksum functions (such as check digit and cheque bit) that are used all the time, to chase out errors in information.
Microsoft has fabricated PowerShell available for macOS 10.thirteen or newer, and Linux, too, but if the thought of using something that originated with Windows gives you lot the heebie-jeebies, know that you can practise the same natively on either OS, too.
macOS
For Mac users, you lot need to fire upwardly the Terminal app, which is in the Utilities folder in Applications. The commands to enter is shasum -a 256, followed by the accost for the file you want to cheque (or just drag and drib into the Terminal window).
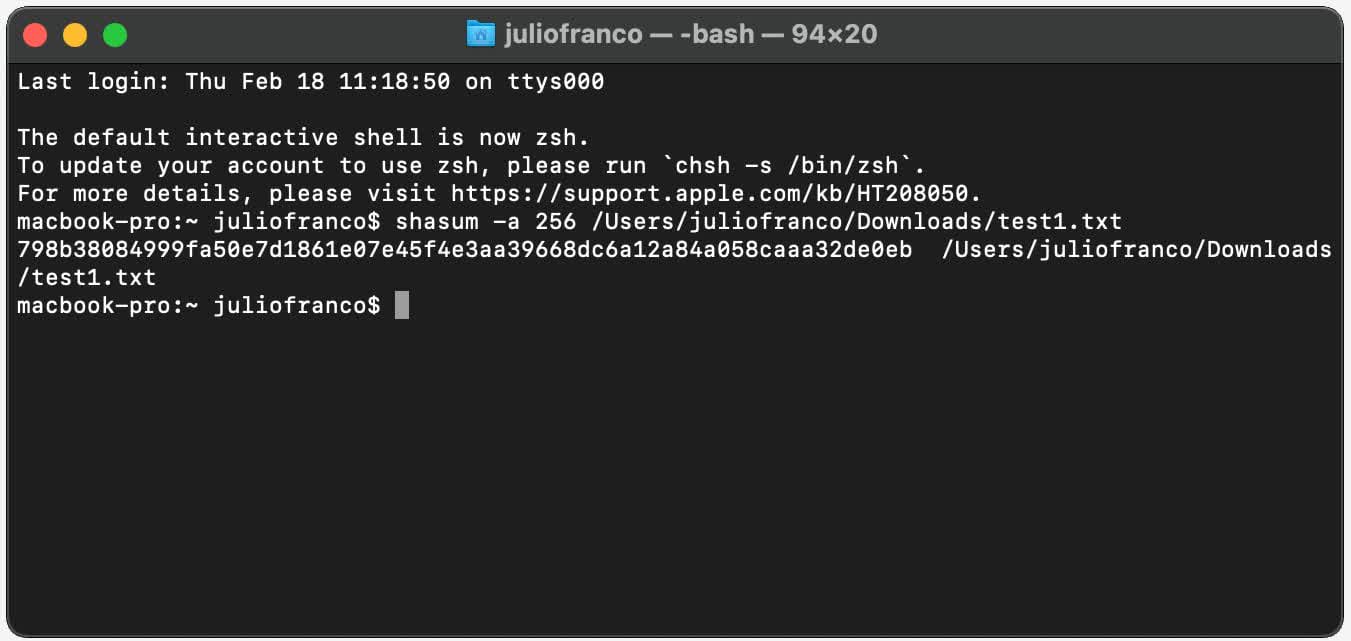
The shasum didactics is the equivalent to Get-FileHash in PowerShell, and the '-a 256' role is there to bespeak which algorithm to apply: i for SHA-1, 256 for SHA-256, and 512 for SHA-512.
Observe how information technology's given us the same checksum for the exam file, every bit we got using PowerShell in Windows? That's the existent power of it: no matter what computer or file organisation you apply, as long as the algorithm is the aforementioned, you'll always get hash values that can be directly compared.
Linux
If you favor the delights of Linux, you'll exist pleased to know that it'southward the same process equally to a higher place -- fire upwards the Terminal and enter sha1sum, sha256sum, or sha512sum followed past the file'due south address to generate the required hash.

Over again, you can run across that we've got the aforementioned checksum for our text file. All runs are doing the exact same math to create the hash, so none of this shouldn't have come up equally a surprise, just information technology's comforting to know that checksums tin be done on any calculating device.
Adding power to your downloads
Given how quick and like shooting fish in a barrel checksums are, information technology's peradventure a fiddling surprising that nosotros don't carry them out more often or at all.
While the likes of Steam handle the process for us automatically, nosotros are reliant on file hosts providing accurate checksums for the data they provide. In the example of TechSpot downloads, for instance, we don't explicitly provide a checksum but the tools that we use to certify that downloads are clean, such equally VirusTotal, use checksum to verify files' integrity and aggregate data when several parties browse the same file over time.
Some websites provide checksums for every file, whereas others only do it for important or very large items (east.1000. Microsoft in their secure download sections), only it's becoming an increasingly rare sight. There are various possible reasons for this, such every bit people simply not beingness aware of them.
Simply where hosts exercise offer information technology, and then at least you lot now know how you tin use the hash -- any actress thing to give y'all a bit more piece of mind is e'er a good matter.
Source: https://www.techspot.com/article/2199-what-is-checksum/
Posted by: romriellsignatich.blogspot.com


0 Response to "What Is a Checksum, and What Can You Do With It?"
Post a Comment